Many production systems control product routings manually. A bill of materials and job routing will be developed for a product. It will be printed out and carried along with a product batch, through a factory and various manufacturing operations. This requires planners, supervisors and production operators to review each product routing and also to decide what should happen next to the product batch.
By connecting manufacturing processes together, a software system can perform all of this product routing. It can communicate directly with production machinery to select the correct production process for each product batch.
Optimising Product Routing
When all production equipment is connected to the production system, the software application controlling the process has a large amount of data about the machinery and production equipment, throughout the entire production process.
In addition, a software application can perform far more analytics and quality checking on products as they progress through the factory. Product routings can be changed based on feedback from production data, or on data from production machinery further down the production line.
The production software can optimise the production process by adding logic to change routing when:
- Bottlenecks can be avoided by balancing product routing against current process times.
- When sales order volume changes, the product can be rerouted automatically through the fastest path to delivery.
- New products can be routed quicker, with less manual decision making on the shop floor.
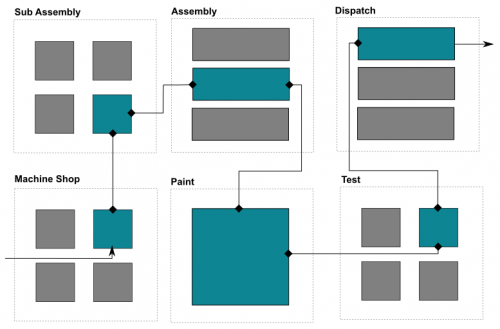
An example software HMI layout of a production facility with product routings highlighted.
Automatic Delivery of Job Packs
The software controlling the production systems knows all the production information about the part coming in to be manufactured. Therefore, it can be connected to CAD and ERP systems to deliver the full job pack with manufacturing information, for the production operator.
This ensures that the correct information is delivered for each product when it is required. It also makes the production of small batches of product easier.
Guided Assembly
Human Machine Interfaces (HMIs) can be used to display production work instructions, guiding the operator through any manual production process. It displays production feedback from machinery that is needed for any decision making that the operator must make.
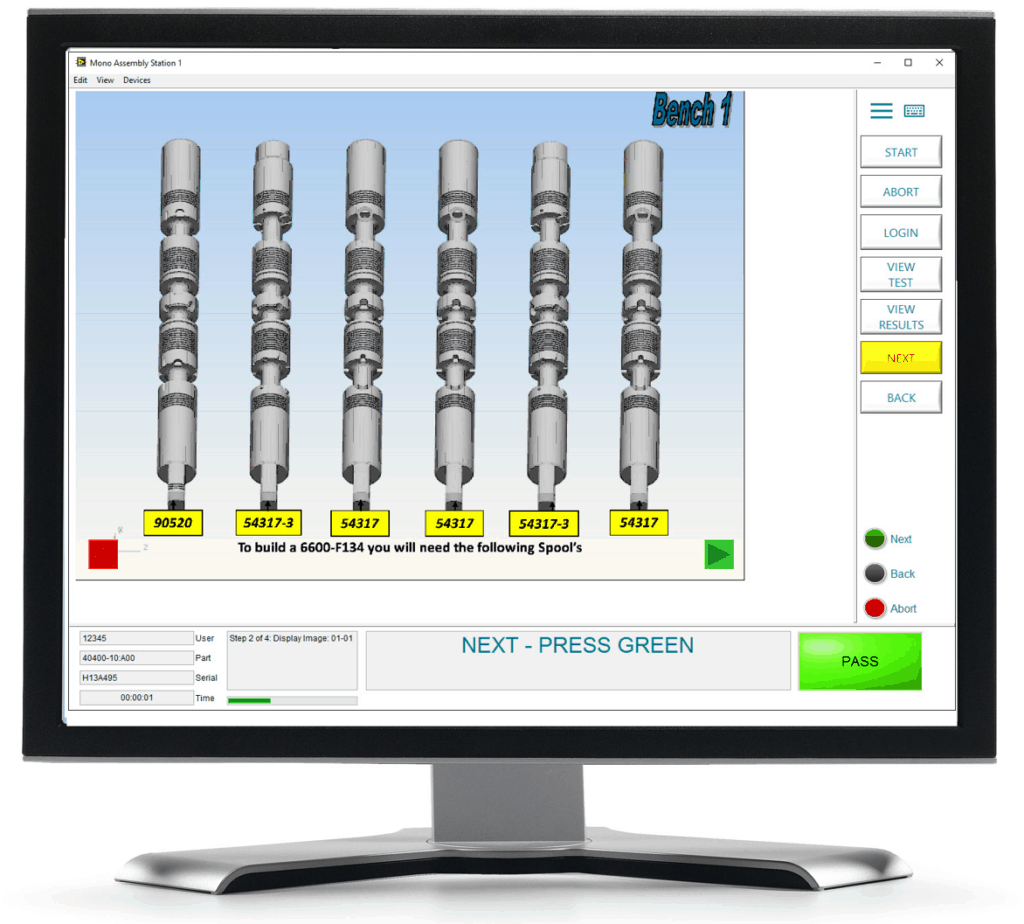
A Production Line HMI
When guided assembly stations are combined with sensors, barcode scanners and RFID tag readers, a trackable and traceable production line can be built. As the product moves along the production line, the software system will record each manufacturing operation that has been completed. It can also record component details that have been used in the product.
All this information can be stored in a production database, so that product reports can be generated detailing all manufacturing operations performed and all components used during manufacture.
Key benefits of connecting production operations
- Producing new products and products with low batch sizes quickly, as production planning and production data can be controlled through the production software.
- Track and Trace production lines with all manufacturing operations recorded and components used.
- Generating production reports for products and batches of product
- Insight into the current production status by viewing production data.
Read the next part of the guide: Part 4 – Improving Your Business With Production Data Analytics




Your blog so nice because This blog gives us knowledge about block diagram